Redundant Power Supply
What is the Redundant Power Supply?
The redundant power supply (RPS) is one of the advanced power supply systems that are designed specifically for preventing power supply failure. Although sometimes people refer to the RPS as the uninterrupted power supply (UPS), RPSs and UPSs are actually different. It is commonly seen on electrical equipment and electronic appliances such as industrial computers, servers, automation control systems, and devices whose power disruption needs to be avoided. With this type of unit, the attached device is free from temporary system failure and/or equipment damage.
How does it Work?
A redundant power supply is a backup power source in the circuit. There can be one primary source and more than one redundant source in a circuit. Since each one of the power sources in the system is able to operate the attached device on its own, the whole system is not going to fail even when one of the sources shut down for any unexpected reason. Under normal circumstances, all power sources share a load of utility power drawn by the device.
Differences between a Redundant Power Supply and Backup Power Supply
The redundant power supply and backup power supply are both considered types of uninterrupted power systems, but they run in a different way. When the primary power supply shuts down, another redundant power supply takes over the role of primary and powers the system by itself. However, the backup power supply draws electricity from backup power sources, such as batteries, when the main power grid outages.
Advantages
The key advantage of the Redundant Power Supply is that it allows hot-swapping which replaces the power supply without interfering with the operation of the attached equipment when the main power supply shuts down. This feature is especially advantageous for network equipment, automation system, and industrial applications where the permanent and stable operation of the system is crucial. Implementing the Redundant Power Supply unit eliminates the unnecessary equipment downtime and risk of system failure. Acro develops many types of power supplies for various applications. Contact us right now and we will find the best power supply solution for you.
DIN Rail 40~48W, Single Output, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +5V、+12V、+24V、+48V
Rated Output Power: 40~48W
Dimension:121(D)x40(W)x110(H) mm
DIN Rail 60W, Single Output, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +24V
Rated Output Power:60W
Dimension:121(D)x40(W)x110(H) mm
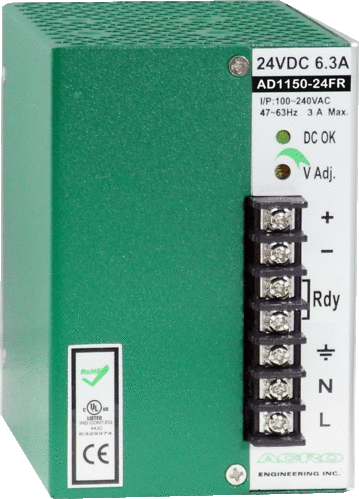
DIN Rail 72W, Single Output, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +12V、+24V、+48V
Rated Output Power: 72W
Dimension:121(D)x56(W)x110(H) mm
DIN Rail 100W, Single Output, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +12V、+24V、+48V
Rated Output Power: 100W
Dimension:110(H)X121(D)X56(W)mm
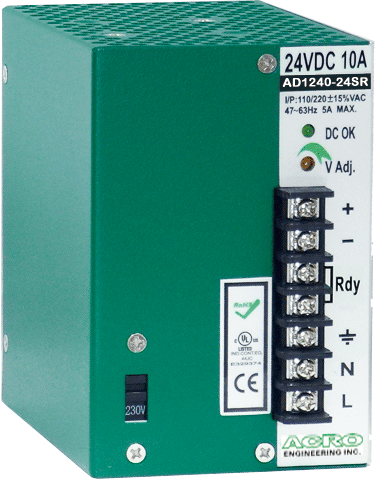
DIN Rail 120W, Single Output, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +12V、+24V、+48V
Rated Output Power: 120W
Dimension:121(D)x75(W)x110(H) mm
DIN Rail 150W, Single Output, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +12V、+24V、+48V
Rated Output Power: 120W
Dimension:100(D)x44.5(W)x107(H) mm
DIN Rail 240W, Single Output, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +12V、+24V、+48V
Rated Output Power: 240W
Dimension:110(H)X121(D)X75(W)mm
DIN Rail 240W, Single Output, Active PFC, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +12V、+24V、+48V
Rated Output Power: 240W
Dimension:121(D)x100(W)x110(H) mm
Active PFC: PF>0.94
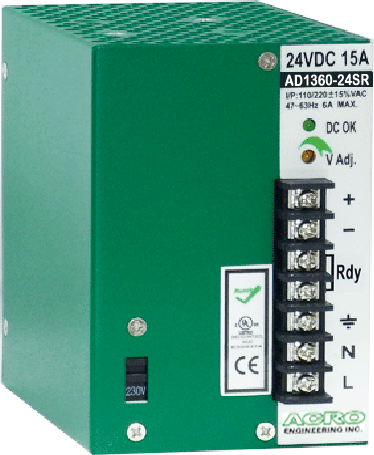
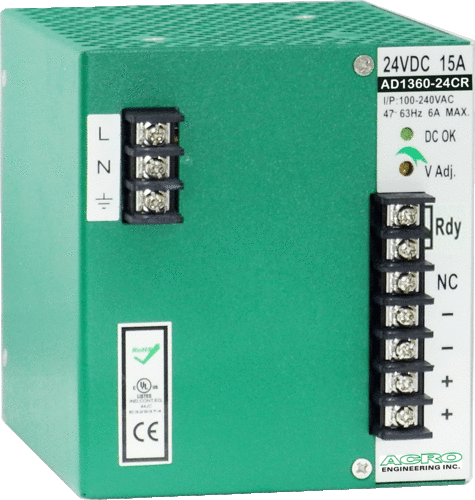
DIN Rail 360W, Single Output, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +24V、+48V
Rated Output Power: 240W
Dimension:110(H)X121(D)X75(W)mm
DIN Rail 360W, Single Output,Active PFC, Redundant function
Rated Output Voltage: +12V、+24V、+48V
Rated Output Power: 360W
Dimension:121(D)x100(W)x110(H) mm
Active PFC: PF>0.94